Main Signs Of Canine Heartworm
Canine heartworm disease is one of the most lethal diseases of pets, which is why it has been the subject of multiple scientific studies. Currently there are effective preventive treatments essential to ensure the welfare of the animal.
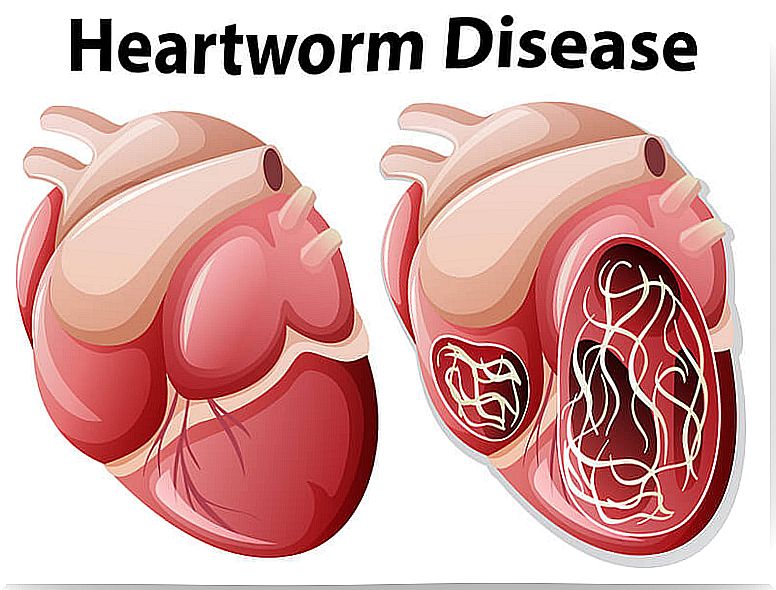
Canine heartworm is a cardiopulmonary disease caused by the Dirofilaria immitis nematode, commonly known as ‘heartworm’. This parasite is located mainly in the host’s right ventricle and pulmonary artery, although it can migrate to other areas of the body in more severe cases.
Besides dogs, cats, wolves, foxes or ferrets are also susceptible to contracting the disease. The transmission of the parasite is vectorial, through a mosquito belonging to the Aedes , Anopheles or Culex genera , among others.
In this way, the mosquito ingests the microfilariae that it will later transmit to the dog through the corresponding bite.
Signs of canine heartworm disease
In the early stages of the disease the animal will not show any apparent symptoms. However, one or several years after infection, the dog will experience the following disorders:
- Mild and persistent cough.
- Resistance to exercise and fatigue after the execution of moderate physical activity.
- Lack of appetite and the consequent loss of weight.
- Heart failure and abdominal bloating due to fluid retention. Both disorders appear when the disease is very advanced.
- Finally, in cases leading to the death of the dog, the so-called caval syndrome will occur. This begins with breathing difficulties, the presence of pale gums, bloody urination and, finally, blockages of blood flow that will lead to heart collapse.
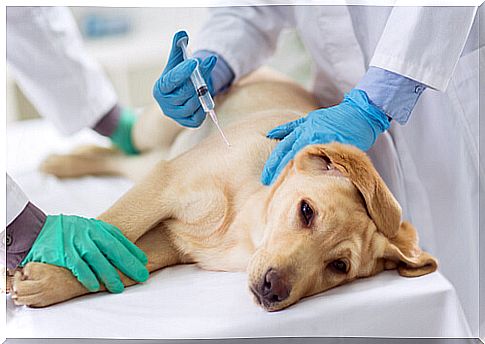
Despite receiving the relevant preventive treatment, dogs must undergo an annual check to detect a possible contagion. The effectiveness of heartworm medications is very high, but must be administered strictly, as missing a single dose can put the animal at risk.
Dogs infected with Dirofilaria immitis can have as many as thirty worms in their hearts, so the higher the number of these, the more severe the symptoms.
Likewise, the diagnosis will be more conclusive the longer the course of the disease and there is an obvious symptomatology. The physical examinations, X – rays, ultrasounds and different types of blood tests will be needed when corroborate the infection.
Precautionary measures
The lethality of canine heartworm makes it essential to carry out adequate prophylactic treatment. There are both oral and topical options or through injections, each with a certain frequency of administration. All of these drugs work by killing immature heartworm larvae, including infectious larvae deposited by the vector mosquito, as well as the next larval stage.
After a period of approximately 51 days, the immature larvae will enter an adult phase against which preventive treatments are ineffective. Due to the short life cycle of this parasite, it is essential to strictly comply with the number of doses prescribed by the veterinarian.

In the event that the dog has been infected, one type or another of protocol will be established depending on the degree of development of the disease and the associated symptoms. Although asymptomatic cases are the most likely to be successful, the severity of the disease does not have to be associated with the severity of the symptoms. In fact, the sickest dogs with the highest number of worms may show the least signs of infection.
Canine heartworm disease is one of the diseases that has caused the most deaths in domestic dogs, which has a global impact. However, it is precisely this impact that has made it possible to carry out an extensive study of it, being rewarded in effective preventive treatments for the animal’s health.