Treatment Of Orchitis In Dogs

Many owners are scared when they perceive that their dogs have swollen and red testicles. These unpleasant symptoms usually indicate the advancement of an infectious process called orchitis. Next, we will explain what orchitis in dogs is and how to treat it to preserve the good health of your best friend.
What is orchitis in dogs?
The genitals of dogs are one of the most sensitive and vulnerable regions of their body, since they can come into contact with dirt and pathogens on a daily basis. Consequently, there is an extensive list of diseases and complications that can affect the genital region of the dog.
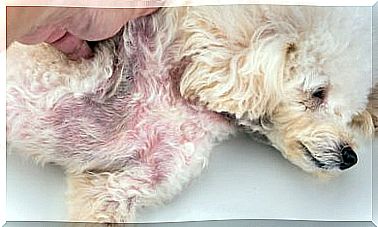
Orchitis in dogs is a type of infection that usually leads to inflammation of the testicles. For this reason, one of the main symptoms associated with this disease is red, swollen and inflamed testicles.
However, not all dogs with inflamed testicles develop orchitis. There are many possible causes for swollen testicles, such as exposure to chemicals. Therefore, it is essential to take your pet to the vet to identify the cause of this anomaly in his genitals.
How do dogs develop orchitis?
In general, the infectious process begins with an injury or burn suffered to the genitals, especially the testicles themselves or the scrotum. For example, if a dog is injured during a fight or suffers a frostbite during the winter.

If this lesion comes into contact with certain bacteria, an infectious process can start. In this way, the wound acts as a ‘gateway’ for bacteria into the dog’s body. Once inside your body, these agents can expand and reach the sperm ducts.
However, the development of an infectious process also usually depends on the state of the immune system of each animal. If the dog has a strengthened immune system, it may come into contact with pathogens and not develop disease.
Symptoms of orchitis in dogs
In addition to red and swollen testicles, dogs with orchitis are often in pain. Consequently, they will hardly allow themselves to be touched or checked in this region and may even prefer to isolate themselves to avoid being manipulated.
Pain, especially if it is intense, also tends to negatively affect the dog’s behavior. Although this may vary from person to person, many dogs are sadder and some can react aggressively.
In addition, the following symptoms associated with orchitis in dogs may be observed:
- Walking with the hind legs wide apart (to avoid touching or rubbing the swollen testicles).
- Presence of pus in the testicles.
- Frequently licking their genitals, especially the testicles.
- Hardening of one or both testicles.
- Slower movements.
- Clumsiness.
- Lethargy.
- Fever.

Treatment of orchitis in dogs
When identifying any symptoms mentioned above or perceiving that your dog has swollen testicles, it is essential to get him quickly to the veterinary center. Only a trained professional will be able to verify the causes of this problem and recommend a specific treatment based on the patient’s needs.
Antibiotics are usually given in the treatment of orchitis to slow down the infectious process and kill pathogenic bacteria. Your vet may also recommend an anti-inflammatory to combat swelling in the testicles and ease the animal’s discomfort.
During the treatment it will be essential that the dog has a clean, comfortable and calm environment to recover more quickly. The absence of traumatic stress will help speed up the effectiveness of the treatment.
How to prevent orchitis in dogs?
First of all, we must prevent as much as possible that our dogs suffer injuries in such a sensitive region. For example, avoid escaping and getting into street fights, or avoid exposing them to the cold and extreme weather changes in winter.
Also remember that optimal hygiene is key to avoid the proliferation of bacteria, fungi, parasites and other pathogens in the home. Therefore, we must not neglect the cleaning and disinfection of the environment and the accessories used by our dogs.
Last but not least, it is essential to offer adequate preventive medicine to our pets throughout their lives. In addition, you have to make preventive visits to the vet every six months, and we must always keep their vaccinations and deworming up to date.